TCP/IP
/ 3 min read
Table of Contents
PROTOCOLS
-
A protocol is a set of rules that must be agreed between the sender and receiver for any communication transmitted over a network .
-
Example:
- Positive voltage represents a bit with value ln Transmission seedThe format of a message
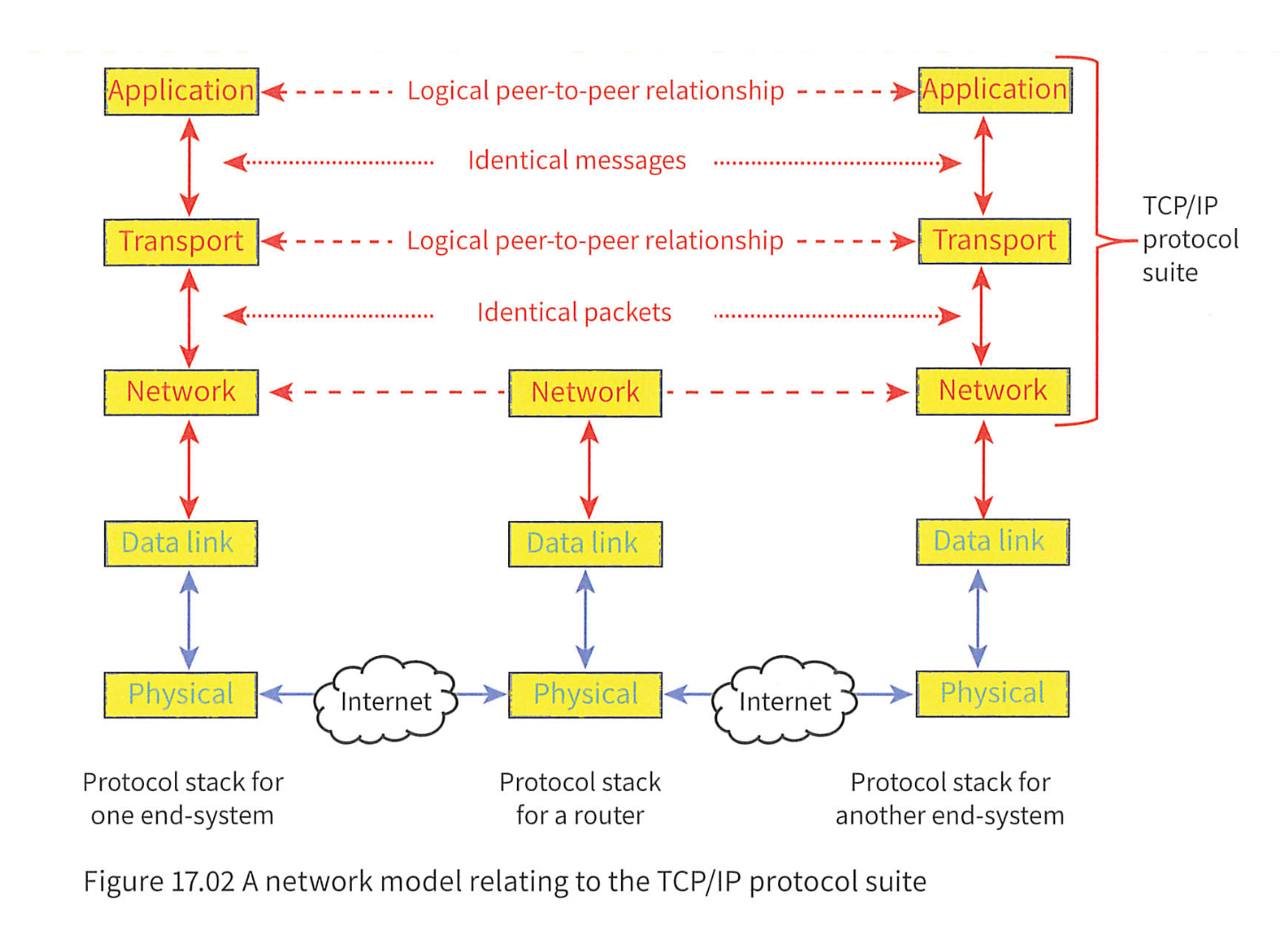
TCP/IP Protocol suite
- TCP/IP is the protocol suite underpinning the internet usage.Without TCP/IP protocol suite the internet would have not been possible.By suite, it means that there are a number of protocols.TCP = transmission control protocolIP= internet protocol
TCP and IP are the 2 main protocols in the suite.TCP/IP specifies how data is Aexchanged over the internet by providing end-to-end communications that identity how it should be broken into packets, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.TCP/IP requires little central management and is designed to make networks reliable with the ability to recover automatically from the failure of any device on the network.

TCP/IP is organized in 4 layers:
The functionality is organized into 4 layers, Which classify all the protocols according to the protocol’s scope of networking.

发送数据
Application: 与用户交互,从用户方接收或发送数据。
Transport layer: 分包 增加端口号
-
Port layer:Marked and seperated for different applications and services runs on the same computer.
-
IP+port number = socket
Internet layer:
Link layer:使用物理链路发送数据包(也可以分为两层)
接收数据
反方向从Lowest 到 Highest
Application Layer
Application layer: HTTP SMTP DNS FTP POP3 IMAP
-
HTTP: Hypertext transfer protocol,
- Pesponsible for corect transfer of webpages on the WWW
-
SMTP: Simple mail transfer protocol.
-
This handles the sending of emails.
-
From email client to email server
-
Between email servers
-
-
РОРЗ
-
Post office protocol
-
This handles the receiving of emails
-
From server to cllent
-
-
IMAP:
-
Internet message access protocol
-
This handles the receiving of emails.
-
From server to client
-
-
FTP
-
File transfer protocol
-
This is a protocol used to transfer computer file between computers
-
It is build on a Client-Server model architecture
-
Transport layer: TCP UDP SCTP
Network layer: IP IGMP ICMP ARP
Data link layer: Ethernet
PEER 2 PEER NETWORK (application layer)
-
The network traffic generated by peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing is one of the main features of Internet use.
-
P2P is an architecture that has no structure and no controlling mechanism.
-
Peers act as both clients and servers and each peer is just one end-system. When a peer acts as a server it is called a ‘seed’
-
The BitTorrent protocol is the most used protocol because it allows fast sharing of files. There are three basic problems to solve if end-systems are using Bit Torrent.
-
How does a peer find others that have the wanted content?
-
How do peers replicate content to provide high-speed downloads for everyone?
-
How do peers encourage other peers to provide content rather just using the protocol to download for themselves?