CS笔记 23.04.12
/ 2 min read
Table of Contents
Unit4: CPU Architecture
Interrupts 中断信号:
-
signal to stop CPU to figure out what to do next
-
allow computer to multitasking 多任务 (不断的切换任务,模拟同时 )
紧急任务需要处理 interrupt signal , 如何判断紧急的程度 priority of interrupt
at the end of F-E cycle, checking if there is an interrupt signal .
-
checking the priority of process , if high enough
-
saving the register and process states into stack .
-
loading the address of ISR (interrupt service routine) into PC,
-
once the ISR is completed, resume the interrupted process and run it continually

RTN register transfer notation
MAR <--- [PC] //the content of PC is copied into MAR by address busMDR <---- [[MAR]] //the content of conent MAR is copied into MDRCIR <---- [MDR] //the content of MDR is copied into CIRPC <-- [PC] + 1 //the content of PC incrementsACC accumulator 累加器
-
contained in ALU
-
to store result during calculation temporarily
IX index register
-
using indexed addressing
-
e.g. finding the address of a [2 ]
SR state register
-
showing the state of result after calcualtion
-
contain 4 flags : zero , negative, overflow, carry out
Von Neumann architecture (stored program concept)
-
CPU , memory , I/O device
-
instruction and data are stored into memory
-
the instruction can be feteched and executed
-
one after another automatically
ALU:
-
arithmetic logic unit, do arithmetic operations,
-
Do logic operations
-
contain ACC register
CU:
-
Control Unit
-
decoding the instruction and sending control signal
IAS
-
immediate access store
-
a piece of memory in CPU to store
-
data and instruction to be executed temporarily
-
Main memory in CPU (Cache)
Bus
-
address bus : transfer address unidirectional
-
data bus : transfer data bidirectional
-
control bus : transfer control signal bidirectional
control signal 控制信号
-
read / write signal to memory
-
system clock 系统时钟
system clock
-
it is an electrical pulse signal to synchronize all the compements
-
in computer system and allow them work together
-
unit : Hz

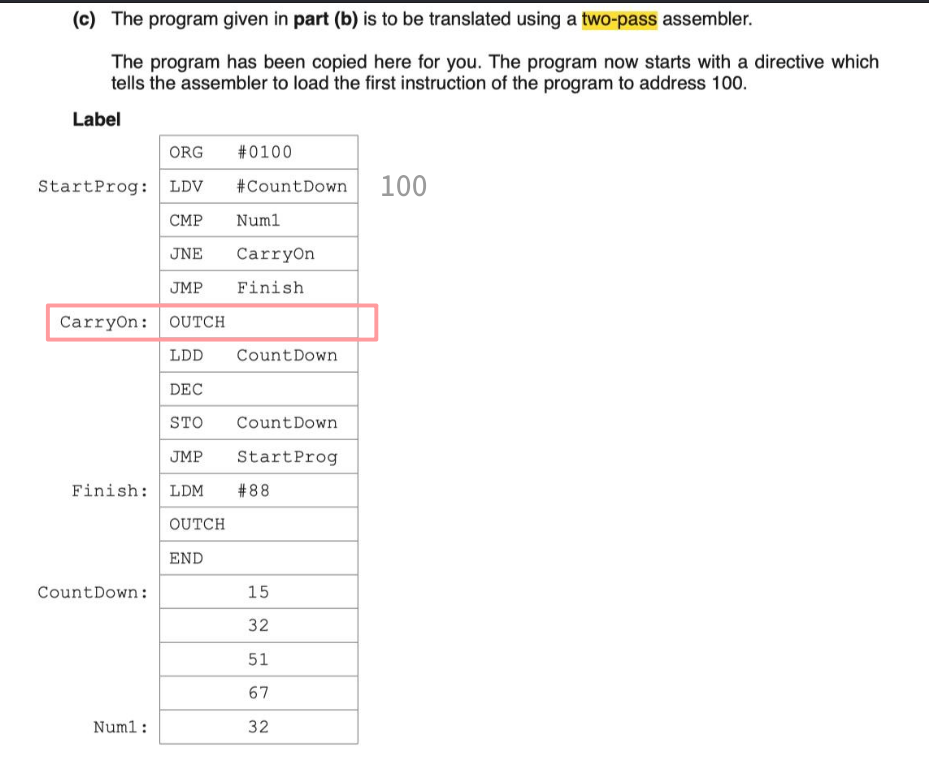
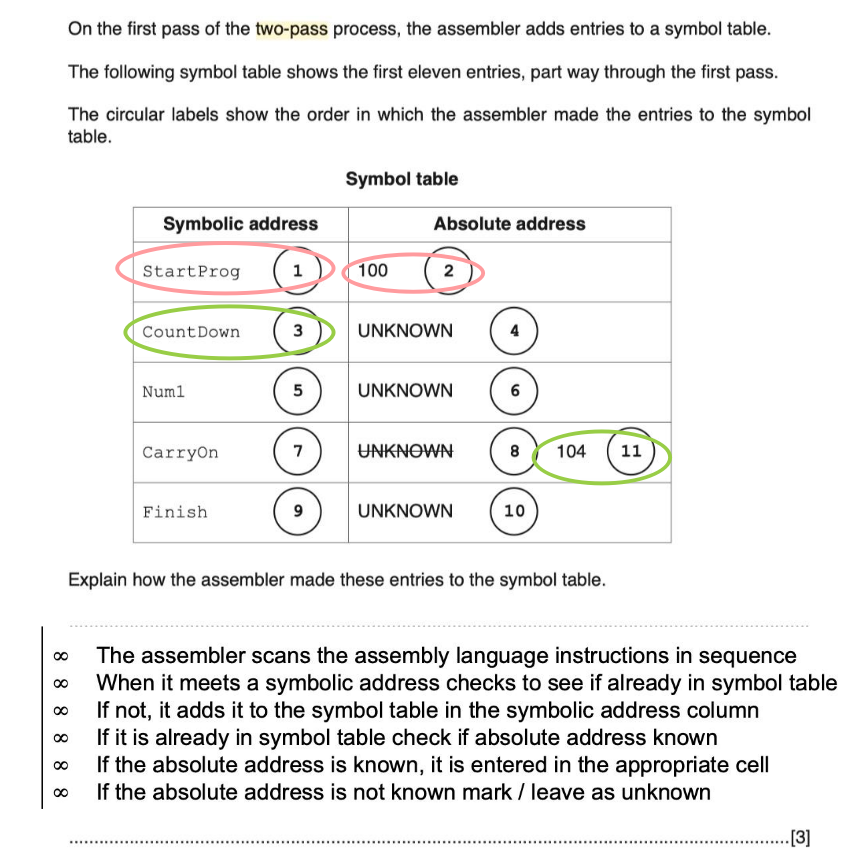
two-pass assembler
one pass
-
reading one line of code at a time
-
allocate the memory for a line of code
-
ignoring unnecessary character like extra space , comments
-
checking if the opcode is valid according to instruction set
-
create / establish symbol table
two-pass
-
reading the souce code line by line
-
translate the souce code into object code / executable file
-
saving or running the object code